1. Hydroponics
The two main functions of soil are to secure plant roots and to allow nutrients to pass into them… so how do plants grow without soil?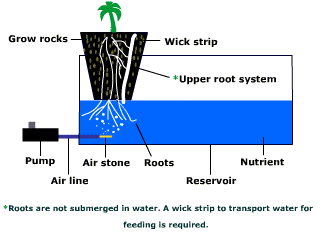
Soil is replaced either with:

- Growing Media Bed System (a tank filled with growing media of some sort). The medium can be pea gravel or expanded clay pellets (3/8-inch to 3/4-inch diameter), which secure the roots. Fiberglass or coconut coir (shredded outer shell) or other fibrous material can also be used but are not as highly recommended.
The media beds are flooded and drained in timed sequence (15 minutes of water saturation per hour) to ensure maximum nutrient and oxygen saturation.
This system is generally more resilient than the others and is suitable for all types of plant growth, but it requires more effort to construct.
Raft System. Plants are secured in cups into holes in polystyrene sheets which float on a nutrient water tank.

Cheap plastic cups with holes or nets work well, or you can buy purpose-built cups. The plants’ roots sit in the water and absorb nutrients. Water is agitated, cycled into a sump tank or aerated to prevent root rot.
This one is easy to construct and best suited for leafy greens—not recommended for heavy feeders like tomatoes.
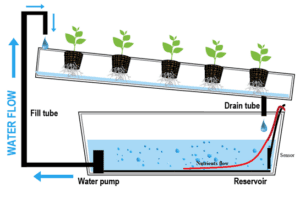
- Continuous Flow or Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) System. This easy-to-construct system dangles the roots of the plants into a continuously flowing stream of nutrient-rich water.
Water is pumped from a tank into a series of channels that gravity-feed back

into the tank. Potential root rot is minimized through the non-immersion of all the roots and the oxygen content of the running water.
Creative and versatile systems can be created using PVC pipes or other materials. Again, this method is best for leafy greens and herbs, not heavy feeding plants like tomatoes.
In all cases, nutrients must be provided in a liquid solution, and they must still be fertilized. Many different organic fertilizers can be bought commercially and dissolved in the water solution, but this is the perfect time to use your homemade biofertilizers, composts, and worm casting extracts (discussed on Day 10).
